Wingpath has ceased trading
We are no longer selling licences for our software products (ModSnmp, ModMultiSim, Modsak, ModSlaveSim, ModMaster and ModTest).
The website will remain operational until at least 2027 for reference purposes, and for the registration and transfer of product licences.
ModSlaveSim - Programmable Modbus slave simulator
ModSlaveSim is a programmable simulator that enables realistic simulation of a single Modbus slave in its environment. Connect your Modbus masters to ModSlaveSim, instead of a real Modbus slave device, in order to test and configure the masters.
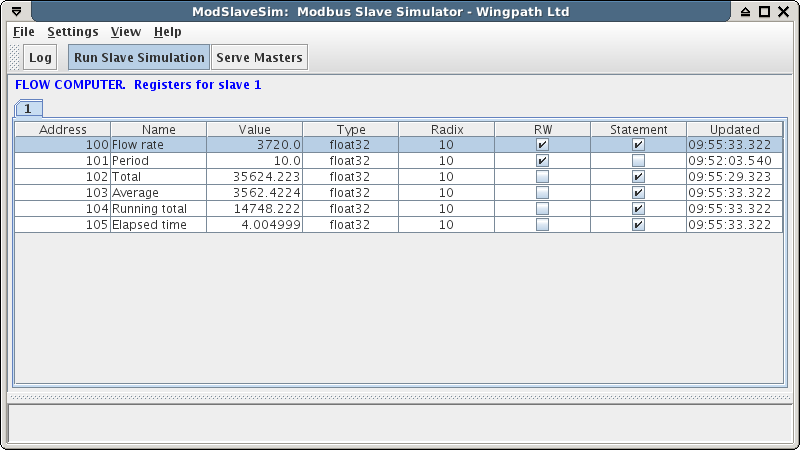
Using a simple control language you can simulate a Modbus slave measuring environment properties (e.g. flow rate), controlling the environment (e.g. opening valves), performing internal calculations (e.g. averages), and responding to Modbus commands from masters.
ModSlaveSim's main features are:
- The Modbus device registers are displayed as they change in the simulation.
- Cross-platform: runs on any system that supports Java JRE 6 or later (serial communications is only supported on Windows, Linux x86 and Raspberry Pi ARM architectures).
- Manual and troubleshooting guide.
- Simulation examples included in the download, which can be loaded from the File menu.
- Informative log of all Modbus messages sent and received providing interpreted data to aid understanding. The log may optionally include register values that have been read, or written to, by a master. The log may also include, or be restricted to, Modbus messages as raw data (in Hex).
- Optional logging to a file, or a window, of Modbus messages sent and received.
- All configuration settings may be saved to, and restored from, a file in XML format.
- Register definitions may be imported and exported in CSV format.
- Full support for coils, discrete inputs, input registers and
holding registers, using the following commands:
- 1 Read Coils
- 2 Read Discrete Inputs
- 3 Read Holding Registers
- 4 Read Input Registers
- 5 Write Single Coil
- 6 Write Single Holding Register
- 8 Diagnostics
- 11 Get Comm Event Counter
- 15 Write Multiple Coils
- 16 Write Multiple Holding Registers
- 17 Report Slave ID
- 22 Mask Write Holding Register
- 23 Read/Write Multiple Holding Registers
- Supports network and serial (RS232/RS422/RS485) interfaces using the following protocol variants:
- Modbus TCP (also known as Modbus TCP/IP)
- Modbus RTU
- Modbus ASCII
- Modbus RTU encapsulated in TCP
- Modbus ASCII encapsulated in TCP
- All known extensions of the Modbus protocol for handling 32-bit and 64-bit integers and floating-point numbers are supported (including Enron/Daniels Modbus).
- Flexible address mapping allows separate or overlaid address spaces (for coils, discrete inputs, input registers, and holding registers) with arbitrary bases.
- Registers can be individually configured for type (integer or float), size (16/32/64-bit), and radix (binary, octal, decimal, or hex).